Java 多线程上下文传递在复杂场景下的实践
作者:vivo互联网技术 查看原文
一、引言
海外商城从印度做起,慢慢的会有一些其他国家的诉求,这个时候需要我们针对当前的商城做一个改造,可以支撑多个国家的商城,这里会涉及多个问题,多语言,多国家,多时区,本地化等等。在多国家的情况下如何把识别出来的国家信息传递下去,一层一层直到代码执行的最后一步。甚至还有一些多线程的场景需要处理。
二、背景技术
2.1 ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal是最容易想到了,入口识别到国家信息后,丢进ThreadLocal,这样后续代码、redis、DB等做国家区分的时候都能使用到。
这里先简单介绍一下ThreadLocal:
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
/**
* Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @return the map
*/
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
/**
* Get the entry associated with key. This method
* itself handles only the fast path: a direct hit of existing
* key. It otherwise relays to getEntryAfterMiss. This is
* designed to maximize performance for direct hits, in part
* by making this method readily inlinable.
*
* @param key the thread local object
* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such
*/
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
- 每一个Thread线程都有属于自己的threadLocals(ThreadLocalMap),里面有一个弱引用的Entry(ThreadLocal,Object)。
- get方法首先通过Thread.currentThread得到当前线程,然后拿到线程的threadLocals(ThreadLocalMap),再从Entry中取得当前线程存储的value。
- set值的时候更改当前线程的threadLocals(ThreadLocalMap)中Entry对应的value值。
实际使用中除了同步方法之外,还有起异步线程处理的场景,这个时候就需要把ThreadLocal的内容从父线程传递给子线程,这个怎么办呢?
不急,Java 还有InheritableThreadLocal来帮我们解决这个问题。
2.2 InheritableThreadLocal
public class InheritableThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {
/**
* Computes the child's initial value for this inheritable thread-local
* variable as a function of the parent's value at the time the child
* thread is created. This method is called from within the parent
* thread before the child is started.
*
* This method merely returns its input argument, and should be overridden
* if a different behavior is desired.
*
* @param parentValue the parent thread's value
* @return the child thread's initial value
*/
protected T childValue(T parentValue) {
return parentValue;
}
/**
* Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
*/
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.inheritableThreadLocals;
}
/**
* Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the table.
*/
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.inheritableThreadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
}
- java.lang.Thread#init(java.lang.ThreadGroup, java.lang.Runnable, java.lang.String, long, java.security.AccessControlContext, boolean)
if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
this.inheritableThreadLocals =
ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
- InheritableThreadLocal操作的是inheritableThreadLocals这个变量,而不是ThreadLocal操作的threadLocals变量。
- 创建新线程的时候会检查父线程中parent.inheritableThreadLocals变量是否为null,如果不为null则复制一份parent.inheritableThreadLocals的数据到子线程的this.inheritableThreadLocals中去。
- 因为复写了getMap(Thread)和CreateMap()方法直接操作inheritableThreadLocals,这样就实现了在子线程中获取父线程ThreadLocal值。
现在在使用多线程的时候,都是通过线程池来做的,这个时候用InheritableThreadLocal可以吗?会有什么问题吗?先看下下面的代码的执行情况:
- test
static InheritableThreadLocal inheritableThreadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
inheritableThreadLocal.set("i am a inherit parent");
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(inheritableThreadLocal.get());
}
});
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
inheritableThreadLocal.set("i am a new inherit parent");// 设置新的值
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(inheritableThreadLocal.get());
}
});
}
i am a inherit parent
i am a inherit parent
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
inheritableThreadLocal.set("i am a inherit parent");
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(inheritableThreadLocal.get());
inheritableThreadLocal.set("i am a old inherit parent");// 子线程中设置新的值
}
});
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
inheritableThreadLocal.set("i am a new inherit parent");// 主线程设置新的值
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(inheritableThreadLocal.get());
}
});
}
i am a inherit parent
i am a old inherit parent
这里看第一个执行结果,发现主线程第二次设置的值,没有改掉,还是第一次设置的值“i am a inherit parent”,这是什么原因呢?
再看第二个例子的执行结果,发现在第一个任务中设置的“i am a old inherit parent"的值,在第二个任务中打印出来了。这又是什么原因呢?
回过头来看看上面的源码,在线程池的情况下,第一次创建线程的时候会从父线程中copy inheritableThreadLocals中的数据,所以第一个任务成功拿到了父线程设置的”i am a inherit parent“,第二个任务执行的时候复用了第一个任务的线程,并不会触发复制父线程中的inheritableThreadLocals操作,所以即使在主线程中设置了新的值,也会不生效。同时get()方法是直接操作inheritableThreadLocals这个变量的,所以就直接拿到了第一个任务设置的值。
那遇到线程池应该怎么办呢?
2.3 TransmittableThreadLocal
TransmittableThreadLocal(TTL)这个时候就派上用场了。这是阿里开源的一个组件,我们来看看它怎么解决线程池的问题,先来一段代码,在上面的基础上修改一下,使用TransmittableThreadLocal。
static TransmittableThreadLocal transmittableThreadLocal = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();// 使用TransmittableThreadLocal
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
executorService = TtlExecutors.getTtlExecutorService(executorService); // 用TtlExecutors装饰线程池
transmittableThreadLocal.set("i am a transmittable parent");
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(transmittableThreadLocal.get());
transmittableThreadLocal.set("i am a old transmittable parent");// 子线程设置新的值
}
});
System.out.println(transmittableThreadLocal.get());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
transmittableThreadLocal.set("i am a new transmittable parent");// 主线程设置新的值
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(transmittableThreadLocal.get());
}
});
}
i am a transmittable parent
i am a transmittable parent
i am a new transmittable parent
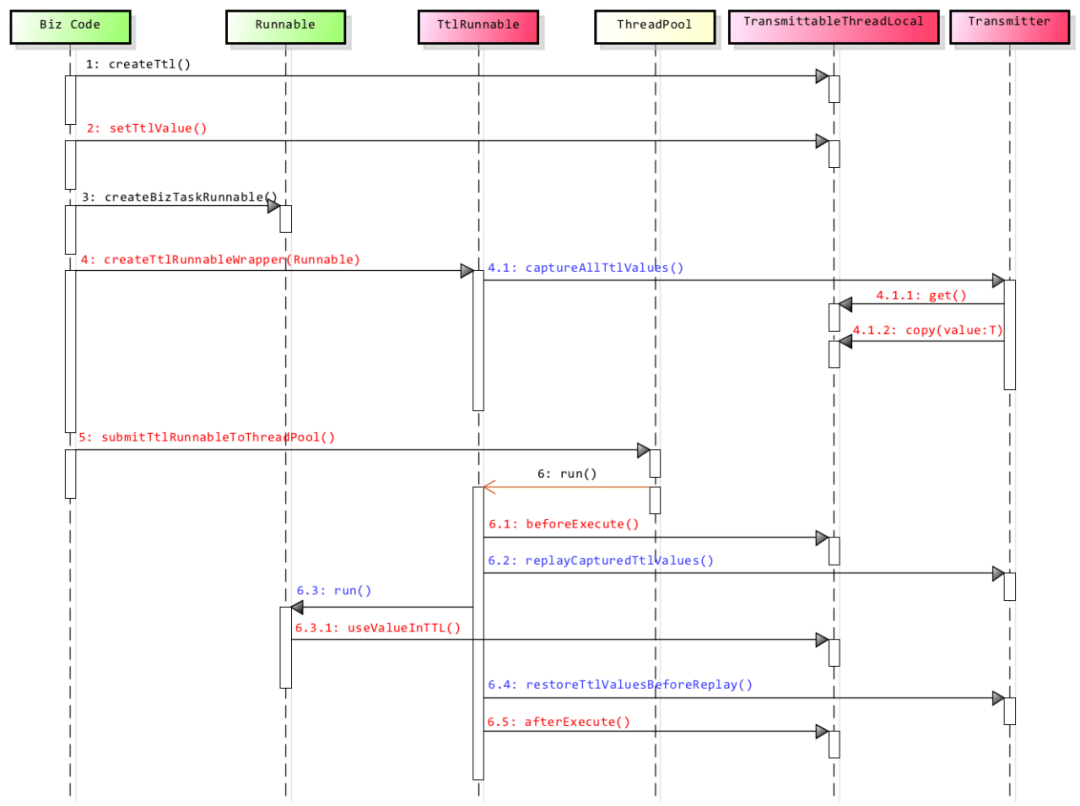
执行代码后发现,使用TransmittableThreadLocal和TtlExecutors.getTtlExecutorService(executorService)装饰线程池之后,在每次调用任务的时,都会将当前的主线程的TransmittableThreadLocal数据copy到子线程里面,执行完成后,再清除掉。同时子线程里面的修改回到主线程时其实并没有生效。这样可以保证每次任务执行的时候都是互不干涉的。这是怎么做到的呢?来看源码。
- TtlExecutors和TransmittableThreadLocal源码
private TtlRunnable(Runnable runnable, boolean releaseTtlValueReferenceAfterRun) {
this.capturedRef = new AtomicReference(capture());
this.runnable = runnable;
this.releaseTtlValueReferenceAfterRun = releaseTtlValueReferenceAfterRun;
}
com.alibaba.ttl.TtlRunnable#run
/**
* wrap method {@link Runnable#run()}.
*/
@Override
public void run() {
Object captured = capturedRef.get();// 获取线程的ThreadLocalMap
if (captured == null || releaseTtlValueReferenceAfterRun && !capturedRef.compareAndSet(captured, null)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("TTL value reference is released after run!");
}
Object backup = replay(captured);// 暂存当前子线程的ThreadLocalMap到backup
try {
runnable.run();
} finally {
restore(backup);// 恢复线程执行时被改版的Threadlocal对应的值
}
}
com.alibaba.ttl.TransmittableThreadLocal.Transmitter#replay
/**
* Replay the captured {@link TransmittableThreadLocal} values from {@link #capture()},
* and return the backup {@link TransmittableThreadLocal} values in current thread before replay.
*
* @param captured captured {@link TransmittableThreadLocal} values from other thread from {@link #capture()}
* @return the backup {@link TransmittableThreadLocal} values before replay
* @see #capture()
* @since 2.3.0
*/
public static Object replay(Object captured) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map>, Object> capturedMap = (Map>, Object>) captured;
Map>, Object> backup = new HashMap>, Object>();
for (Iterator extends Map.Entry>, ?>> iterator = holder.get().entrySet().iterator();
iterator.hasNext(); ) {
Map.Entry>, ?> next = iterator.next();
TransmittableThreadLocal> threadLocal = next.getKey();
// backup
backup.put(threadLocal, threadLocal.get());
// clear the TTL value only in captured
// avoid extra TTL value in captured, when run task.
if (!capturedMap.containsKey(threadLocal)) {
iterator.remove();
threadLocal.superRemove();
}
}
// set value to captured TTL
for (Map.Entry>, Object> entry : capturedMap.entrySet()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
TransmittableThreadLocal threadLocal = (TransmittableThreadLocal) entry.getKey();
threadLocal.set(entry.getValue());
}
// call beforeExecute callback
doExecuteCallback(true);
return backup;
}
com.alibaba.ttl.TransmittableThreadLocal.Transmitter#restore
/**
* Restore the backup {@link TransmittableThreadLocal} values from {@link Transmitter#replay(Object)}.
*
* @param backup the backup {@link TransmittableThreadLocal} values from {@link Transmitter#replay(Object)}
* @since 2.3.0
*/
public static void restore(Object backup) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map>, Object> backupMap = (Map>, Object>) backup;
// call afterExecute callback
doExecuteCallback(false);
for (Iterator extends Map.Entry>, ?>> iterator = holder.get().entrySet().iterator();
iterator.hasNext(); ) {
Map.Entry>, ?> next = iterator.next();
TransmittableThreadLocal> threadLocal = next.getKey();
// clear the TTL value only in backup
// avoid the extra value of backup after restore
if (!backupMap.containsKey(threadLocal)) {
iterator.remove();
threadLocal.superRemove();
}
}
// restore TTL value
for (Map.Entry>, Object> entry : backupMap.entrySet()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
TransmittableThreadLocal threadLocal = (TransmittableThreadLocal) entry.getKey();
threadLocal.set(entry.getValue());
}
}
可以看下整个过程的完整时序图:
OK,既然问题都解决了,来看看实际使用吧,有两种使用,先看第一种,涉及HTTP请求、Dubbo请求和 job,采用的是数据级别的隔离。
三、 TTL 在海外商城的实际应用
3.1 不分库,分数据行 + SpringMVC
用户 HTTP 请求,首先我们要从url或者cookie中解析出国家编号,然后在TransmittableThreadLocal中存放国家信息,在 MyBatis 的拦截器中读取国家数据,进行sql改造,最终操作指定的国家数据,多线程场景下用TtlExecutors包装原有自定义线程池,保障在使用线程池的时候能够正确将国家信息传递下去。
- HTTP 请求
public class ShopShardingHelperUtil {
private static TransmittableThreadLocal<String> countrySet = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();
/**
* 获取threadLocal中设置的国家标志
* @return
*/
public static String getCountry() {
return countrySet.get();
}
/**
* 设置threadLocal中设置的国家
*/
public static void setCountry (String country) {
countrySet.set(country.toLowerCase());
}
/**
* 清除标志
*/
public static void clear () {
countrySet.remove();
}
}
/** 拦截器对cookie和url综合判断国家信息,放入到TransmittableThreadLocal中 **/
// 设置线程中的国家标志
String country = localeContext.getLocale().getCountry().toLowerCase();
ShopShardingHelperUtil.setCountry(country);
/** 自定义线程池,用TtlExecutors包装原有自定义线程池 **/
public static Executor getExecutor() {
if (executor == null) {
synchronized (TransmittableExecutor.class) {
if (executor == null) {
executor = TtlExecutors.getTtlExecutor(initExecutor());// 用TtlExecutors装饰Executor,结合TransmittableThreadLocal解决异步线程threadlocal传递问题
}
}
}
return executor;
}
/** 实际使用线程池的地方,直接调用执行即可**/
TransmittableExecutor.getExecutor().execute(new BatchExeRunnable(param1,param2));
/** mybatis的Interceptor代码, 使用TransmittableThreadLocal的国家信息,改造原有sql,加上国家参数,在增删改查sql中区分国家数据 **/
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler) invocation.getTarget();
BoundSql boundSql = statementHandler.getBoundSql();
String originalSql = boundSql.getSql();
Statement statement = (Statement) CCJSqlParserUtil.parse(originalSql);
String threadCountry = ShopShardingHelperUtil.getCountry();
// 线程中的国家不为空才进行处理
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(threadCountry)) {
if (statement instanceof Select) {
Select selectStatement = (Select) statement;
VivoSelectVisitor vivoSelectVisitor = new VivoSelectVisitor(threadCountry);
vivoSelectVisitor.init(selectStatement);
} else if (statement instanceof Insert) {
Insert insertStatement = (Insert) statement;
VivoInsertVisitor vivoInsertVisitor = new VivoInsertVisitor(threadCountry);
vivoInsertVisitor.init(insertStatement);
} else if (statement instanceof Update) {
Update updateStatement = (Update) statement;
VivoUpdateVisitor vivoUpdateVisitor = new VivoUpdateVisitor(threadCountry);
vivoUpdateVisitor.init(updateStatement);
} else if (statement instanceof Delete) {
Delete deleteStatement = (Delete) statement;
VivoDeleteVisitor vivoDeleteVisitor = new VivoDeleteVisitor(threadCountry);
vivoDeleteVisitor.init(deleteStatement);
}
Field boundSqlField = BoundSql.class.getDeclaredField("sql");
boundSqlField.setAccessible(true);
boundSqlField.set(boundSql, statement.toString());
} else {
logger.error("----------- intercept not-add-country sql.... ---------" + statement.toString());
}
logger.info("----------- intercept query new sql.... ---------" + statement.toString());
// 调用方法,实际上就是拦截的方法
Object result = invocation.proceed();
return result;
}
对于 Dubbo 接口和无法判断国家信息的 HTTP 接口,在入参部分增加国家信息参数,通过拦截器或者手动set国家信息到TransmittableThreadLocal。
对于定时任务job,因为所有国家都需要执行,所以会把所有国家进行遍历执行,这也可以通过简单的注解来解决。
这个版本的改造,点检测试也基本通过了,自动化脚本验证也是没问题的,不过因为业务发展问题最终没上线。
3.2 分库 + SpringBoot
后续在建设新的国家商城的时候,分库分表方案调整为每个国家独立数据库,同时整体开发框架升级到SpringBoot,我们把这套方案做了升级,总体思路是一样的,只是在实现细节上略有不同。
SpringBoot 里面的异步一般通过 @Async这个注解来实现,通过自定义线程池来包装,使用时在 HTTP 请求判断locale信息的写入国家信息,后续完成切DB的操作。
对于 Dubbo 接口和无法判断国家信息的 HTTP 接口,在入参部分增加国家信息参数,通过拦截器或者手动set国家信息到TransmittableThreadLocal。
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor(){
return TtlThreadPoolExecutors.getAsyncExecutor();
}
public class TtlThreadPoolExecutors {
private static final String COMMON_BUSINESS = "COMMON_EXECUTOR";
public static final int QUEUE_CAPACITY = 20000;
public static ExecutorService getExecutorService() {
return TtlExecutorServiceMananger.getExecutorService(COMMON_BUSINESS);
}
public static ExecutorService getExecutorService(String threadGroupName) {
return TtlExecutorServiceMananger.getExecutorService(threadGroupName);
}
public static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor getAsyncExecutor() {
// 用TtlExecutors装饰Executor,结合TransmittableThreadLocal解决异步线程threadlocal传递问题
return getTtlThreadPoolTaskExecutor(initTaskExecutor());
}
private static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor initTaskExecutor () {
return initTaskExecutor(TtlThreadPoolFactory.DEFAULT_CORE_SIZE, TtlThreadPoolFactory.DEFAULT_POOL_SIZE, QUEUE_CAPACITY);
}
private static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor initTaskExecutor (int coreSize, int poolSize, int executorQueueCapacity) {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(coreSize);
taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(poolSize);
taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(executorQueueCapacity);
taskExecutor.setKeepAliveSeconds(120);
taskExecutor.setAllowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
taskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix("TaskExecutor-ttl");
taskExecutor.initialize();
return taskExecutor;
}
private static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor getTtlThreadPoolTaskExecutor(ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor) {
if (null == executor || executor instanceof ThreadPoolTaskExecutorWrapper) {
return executor;
}
return new ThreadPoolTaskExecutorWrapper(executor);
}
}
/**
* @ClassName : LocaleContextHolder
* @Description : 本地化信息上下文holder
*/
public class LocalizationContextHolder {
private static TransmittableThreadLocal localizationContextHolder = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();
private static LocalizationInfo defaultLocalizationInfo = new LocalizationInfo();
private LocalizationContextHolder(){}
public static LocalizationContext getLocalizationContext() {
return localizationContextHolder.get();
}
public static void resetLocalizationContext () {
localizationContextHolder.remove();
}
public static void setLocalizationContext (LocalizationContext localizationContext) {
if(localizationContext == null) {
resetLocalizationContext();
} else {
localizationContextHolder.set(localizationContext);
}
}
public static void setLocalizationInfo (LocalizationInfo localizationInfo) {
LocalizationContext localizationContext = getLocalizationContext();
String brand = (localizationContext instanceof BrandLocalizationContext ?
((BrandLocalizationContext) localizationContext).getBrand() : null);
if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(brand)) {
localizationContext = new SimpleBrandLocalizationContext(localizationInfo, brand);
} else if(localizationInfo != null) {
localizationContext = new SimpleLocalizationContext(localizationInfo);
} else {
localizationContext = null;
}
setLocalizationContext(localizationContext);
}
public static void setDefaultLocalizationInfo(@Nullable LocalizationInfo localizationInfo) {
LocalizationContextHolder.defaultLocalizationInfo = localizationInfo;
}
public static LocalizationInfo getLocalizationInfo () {
LocalizationContext localizationContext = getLocalizationContext();
if(localizationContext != null) {
LocalizationInfo localizationInfo = localizationContext.getLocalizationInfo();
if(localizationInfo != null) {
return localizationInfo;
}
}
return defaultLocalizationInfo;
}
public static String getCountry(){
return getLocalizationInfo().getCountry();
}
public static String getTimezone(){
return getLocalizationInfo().getTimezone();
}
public static String getBrand(){
return getBrand(getLocalizationContext());
}
public static String getBrand(LocalizationContext localizationContext) {
if(localizationContext == null) {
return null;
}
if(localizationContext instanceof BrandLocalizationContext) {
return ((BrandLocalizationContext) localizationContext).getBrand();
}
throw new LocaleException("unsupported localizationContext type");
}
}
@Override
public LocaleContext resolveLocaleContext(final HttpServletRequest request) {
parseLocaleCookieIfNecessary(request);
LocaleContext localeContext = new TimeZoneAwareLocaleContext() {
@Override
public Locale getLocale() {
return (Locale) request.getAttribute(LOCALE_REQUEST_ATTRIBUTE_NAME);
}
@Override
public TimeZone getTimeZone() {
return (TimeZone) request.getAttribute(TIME_ZONE_REQUEST_ATTRIBUTE_NAME);
}
};
// 设置线程中的国家标志
setLocalizationInfo(request, localeContext.getLocale());
return localeContext;
}
private void setLocalizationInfo(HttpServletRequest request, Locale locale) {
String country = locale!=null?locale.getCountry():null;
String language = locale!=null?(locale.getLanguage() + "_" + locale.getVariant()):null;
LocaleRequestMessage localeRequestMessage = localeRequestParser.parse(request);
final String countryStr = country;
final String languageStr = language;
final String brandStr = localeRequestMessage.getBrand();
LocalizationContextHolder.setLocalizationContext(new BrandLocalizationContext() {
@Override
public String getBrand() {
return brandStr;
}
@Override
public LocalizationInfo getLocalizationInfo() {
return LocalizationInfoAssembler.assemble(countryStr, languageStr);
}
});
}
对于定时任务job,因为所有国家都需要执行,所以会把所有国家进行遍历执行,这也可以通过简单的注解和AOP来解决。
四、总结
本文从业务拓展的角度阐述了在复杂业务场景下如何通过ThreadLocal,过渡到InheritableThreadLocal,再通过TransmittableThreadLocal解决实际业务问题。因为海外的业务在不断的探索中前进,技术也在不断的探索中演进,面对这种复杂多变的情况,我们的应对策略是先做国际化,再做本地化,more global才能more local,多国家的隔离只是国际化最基本的起点,未来还有很多业务和技术等着我们去挑战。
